Apple Inc.: Strategic Plan
Introduction
The main objective of this report is to prepare a strategic plan for Apple by concentrating on the model of David Fred. However, this paper focuses on the vision and mission of the company, external opportunities and threats, competitive environment, internal strengths and weaknesses, long- terms objectives and so on. At the same time, this paper highlights on an opportunity, alternative strategies, situation analysis, strategic formulation, application and control, IFE matrix, QSPM and SPACE matrix, Grand strategy matrix, Competitive Profile Matrix and so on. This paper concentrates on single opportunity that is the prospect of i-phone in the global smartphone market as iPhone sales revenue increased by 266% in 2009 (Apple Inc, 2010).
Background of Apple
Apple Inc. established in 1976 by Steve Jobs and Steve Wonzniak, which is now one of the bestsellers of computers, communicating and entertainment devices like i-phone, i-pad, Smartphones, etc. specializing in creation, promotion, and R&D together with applicable software, equipment and prominent networking in order to ascertain utmost customer-satisfaction. The company encompasses a huge range of product line, accompanied be the third-party value added services through Apple’s web based services; additionally, the target customers of the company are governmental agencies, educational institutes, SMB enterprises, as well as individual customers. Most importantly, it is arguable that the business also focuses on multipurpose digital-music and video-systems, engages in the online distribution of audio books, short-films, and television-shows, proffers individual software products, such as Mac-OS X, e Mac, iMac, iBook, video-creation, and markets these with in-house and outsourced software and networking resolution items. This strategic plan will deal with only the opportunity of i-phone.
Vision and Mission of Apple
Apple wants to become the global leader in i-Phone, computer and digital music products in long- run, which is its vision. For this, it wants to introduce the best i-phone, which would be like a mini-computer that is its mission. Such mission has been developed by integrating each part of its broader vision by reflecting most fundamental corporate intentions. It has a great importance since it has the possibility to be accurate and effective decision with a potential to be altered regarding objectives, corporate strategies and behavior. Keeping a close agreement between vision and mission introduces more reliability for Apple. However, basic characteristics of mission incorporate providing superior offerings, innovative technology, meeting higher quality standards, concern for the stakeholders, customers, employees and society. Thus, its generic components are Customers, products or services, technology, markets, need for survival, growth and profitability, self- knowledge, philosophy, concern for personnel and image (WorldPress, 2011).
Mission writing and evaluation
The mission Statement of Apple is, “Bringing the best i-phone experience to students, educators, creative professionals and consumers around the world through its innovative hardware, software and Internet offerings”. This mission reflects all of the integral commitments and objectives that it wants to gain throughout the strategic planning process.
Internal (Strengths & Weaknesses)
Strengths
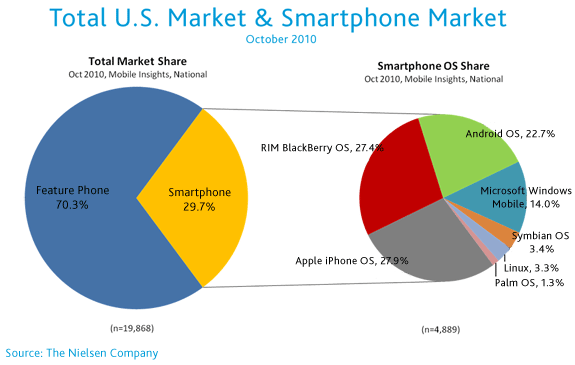
Apple has business operations in highly competitive global smartphone markets and enjoys a market-leading position in the iPhone, mobile, and customer electronics segments and it successfully captured a 27.9% share of the US i-phone market in 2010.
Strong brand awareness and market stability of Apple for the products of iPhone, iPod, and other products with the rapid change of the US market like about 44% of its net sales in 2010 generated from sales to buyers inside the US are the main strength of this company. According to the annual report 2010 of Apple, it had about 46600 full-time permanent workers and an additional 2800 full-time temporary staff and contractors, who have strong educational backgrounds. In addition, it has strong administrative control over the skilled, experienced, and brilliant employees as well as the company. However, this company distributes iPhones in over 89 countries, iTunes Store presently serves customers in 23 nations, and iPad in 26 countries; so, this data demonstrates the bright future of the iPhone in the global market though it has some barriers the outside of the US market. However, Chen, et al (2010, p.10) stated that the quality of Apple’s iPhone is outstanding in aspects of brightness, scratch-resistant screens, well metallic finish, and viruses resistance system. In addition, many companies collapsed for mismanagement, it has maintained the standards of the PCAOB1 in the audit procedure to develop risk management systems, performance plans, other reports, and so on.
Weakness
The financial situation of resellers is one of the most important factors in the sale iPhones as it should require a large fund to continue business with full of confidence while the purchasing power of the buyers has decreased due to global economic downturns, which negatively affected the export market share of iPhone. Competitors like Hewlett Packard, Dell, IBM, Samsung, Compaq and other firms have already created a strong customer base in the smartphone market by joining new features in their similar Smartphone
External (Opportunities & Threats)
Opportunities
As the demand of Apple’s iPhone is increasing dramatically in the outside of the US market, it has huge scope to include more features in single i-phone devise by applying the advance technology and research outcomes though the price of this product is too high. However, it has strong financial capability order to create a large customer base by implementing a cooperative strategy like a joint venture, and merger with multinational companies creates the opportunity to spread out its iPhone business rapidly; for example, the objective of a joint venture agreement between Apple and IBM was to form Taligent to introduce the revolutionary new operating system.
Threats
According to the annual report of 2010 Apple, the economic situation could adversely influence this Company as its operations and performance depend extensively on global financial conditions; so, the company will face challenges if its operating system of iPhone products depends on the performance of distributors, staff and other third parties. On the other hand, competitors are the main threat to Apple’s iPhone as competitors can change customers’ choices by implementing different strategies with quality features, for example, IBM entered in the PC market with pioneer products at competitive price in 1981, and introduction of other similar products reduced the market share of Apple’s iPhone. Other threats are – the market environment being extremely dependent on the rapid technological change, problems to expand its iPhone products in the Asian market, and the risk of legal litigation due to the accession of third parties’ intellectual property. On the other hand, many firms produced similar smartphone products without patents and fix comparatively lower prices, which really a threat to Apple’s iPhone, for instance, Microsoft copied the graphical user interface, and some other companies copy the features of the i-phone and sell without any permission
An Opportunity
This paper concentrates on the prospect of iPhone’s latest model in the global market as this company earned large profit from this product. However, iPhone is a communication device innovated by Apple integrating GSM2 technology and Information Technology where the most popular i-pod functions are added and the users are facilitated to telecommunication and internet applications.
Long-Term Objectives
Apple is intended to increase annual sales revenue from the worldwide operation of key products like the iPhone by 25% within the next five years, so It will increase its annual budget for R&D by 200% within the fiscal year 2016 in order to conduct research more attentively to find out proper solutions over the competitors. In addition, it has aimed to carry on the IMC program to develop customer awareness about the iPhone products of this company by 30% to 45% within the next five years, therefore, it will increase the budget for promotional activities by 80% within the next five years to strengthen the brand image of Apple’s iPhone to the global customers.
The Internal Assessment
Internal audit
Stronger factors of internal audit involve high revenue generation from iPhone, iTunes music store, personal hardware and software, restoring notebooks and desktops, technological sophistication, low debt, etc. Conversely, weaker issues consider less integration with Intel and Microsoft, backward globalization, low profit from high demand items, etc. (Apple Inc, 2010).
Production/ operation, management and marketing
The Company’s operating criteria are run by the production of some products and operation of some services. Major products include iPhone, iPod, iPad, iLife, iWork, Ios, Mac OSX, and TV, etc. Services involve online, app and iTunes stores, Mobile Me and iBooks. It operates five sections, which are liable for developing its offerings along with evaluation and production of computer, software and peripheral tools. Additionally, it holds product assistance sections that are responsible particularly for the marketing, allocation and after-sale support, like- The north American, European, Communications and Markets Marketing Division. Apple also has several administrative divisions for managing its daily organizational affairs, like- The finance, Legal Service and HR divisions (Freedman and Vohr, 1998).
After the period of reorganization, Apple’s i-phone has been trying to make a better fit between its production and marketing strategy. Such efforts have been reflected by the practice of customer-oriented order fulfillment and delivery system, integration with third- parties for software improvement, market penetration through branding and niche marketing, development of the new products through recognizing speech and virtual reality (Freedman and Vohr, 1998).
Finance and accounting perspectives
Apple provides software-enabled for operating the corporate accounting, payroll as well as other organizational requirements on their items. In 2010, Apple-owned $75.18 billion of assets, $47.79 billion of equity, $65.23 billion of revenue, $18.39 billion of income and 14.01 billion of net profit (Apple Inc, 2011).
By analyzing the company’s balance sheet from 2001 to 2005, it can summarize that the sales price has been increased from $1.02 to $3.21, book value from $1.39 to $6.0 and net profit margin from -0.7% to 9.6%. From the same time frame, its book value per share raised from $5.59 to $8.94, debt-equity from 0.08 to 0, ROE (Return on Equity) from null to 17.9% and ROA (Return on Assets) -0.6 to 11.6% (Apple Inc, 2010). However, the following figure shows that Apple’s iPhone captured a 27.9% share of the US market –
Research and development and MIS
The internal and external R and D costs of Apple Inc. has been raised by 20% as $224 million to $1.3 billion from 2008 to 2009. The general reason for which Apple tends to spend such a huge amount is that it wants to have technological sophistication through such practice. Moreover, $11 million has been used for developing software in 2008. Such expenses also assist the company to sharpen its revenue stream, capitalizing on future growth along with actionable position and time-wise expansion of new and modified versions of products as the major part of its organizational strategy.
The role of proper information flow in the company’s MIS system is distinctive since such information assists the company in proper recording, processing, routing and tabulating all the corporate transactions. The MIS department of Apple is responsible for tracking sales data and inventory (Apple Inc, 2011).
IFE matrix
According to the IFE matrix, the key internal strengths and weaknesses of a company’s iPhone segment are weighted and rated, and finally, the overall weighted score is calculated. Based on these considerations, several internal stronger and weaker points of Apple can be listed for the further rating (Apple Inc, 2011), such as-
Value chain analysis
The value chain is the entire process through which the company can create value for its products and services for the final consumers. Thus, the value chain process of Apple Inc. consists of several stages circulating from raw materials suppliers to the users. Those stages involve content, advertising, manufacturing, distribution, hosting, promotion, finding and so on. Through each such stage, the company adds value to its distinctive offerings in terms of associating with various disputes and scopes. Collaboration is one of the most important characteristics of Apple’s value chain. For developing its major products such as iPod along with Macintosh, the complete offer is enclosed within the package by keeping such chain preassemble. By altering the vendor from IBM to Intel for the popular Macintosh, it has improved the performance of the chain by gaining an improved price from the customers than before. By assessing the customers’ preference, Apple’s iPhone basically differentiates this item in terms of quality and promotion for brand development throughout each phase of the value chain. At the international level, it had introduced a “multimodal” strategy with a network model that adjusts the domestic market, and behaves like a local with a mother entity support as a single distribution chain (Freedman and Vohr, 1998).
SPACE matrix
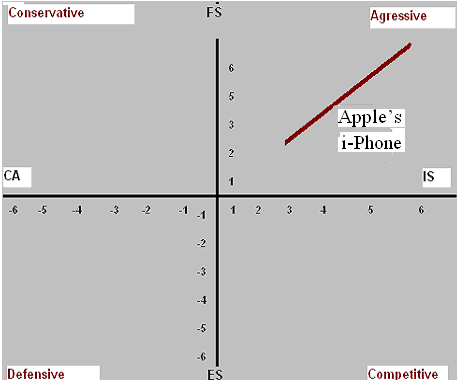
For the strategic evaluation of Apple by SPACE matrix, it is necessary to rate the company’s financial and industrial strength, environmental stability and differential advantage (Apple Inc, 2011), such as
Here, the points to produce the graph is –
X-axis = CA + IS = -10 + 18 = 8
y-axis = FS + ES = 20 – 17 = 3
FS=20.0
IS=18.0
CS= -10.0
ES= -17.0
Decision stages
Decision making for Apple’s iPhone occurs at various phases. For example, it takes rational decisions for choosing options between the strategic alternatives by considering hypothesis, commitment, representation and control. Various phases of decisions involve new features in iPhone products, partnership or collaboration, daily operations, employment and formulation of distribution network decisions,s etc. (Freedman and Vohr, 1998).
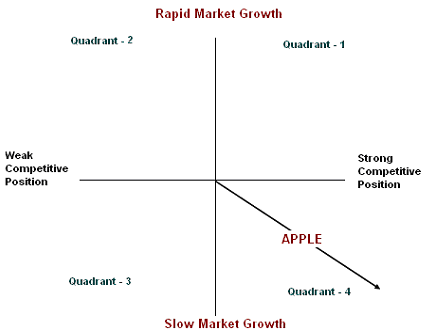
Grand strategy matrix
This model is helpful to determine the corporate position in terms of market growth and position in the market. Among the four quadrants, Apple can be positioned in quadrant four, which shows that the company is in a slow market growth situation with strong competitive positioning global market though it has the strongest growth in the US market. Here, Apple’s iPhone basically occupies a favorable position with the option of corporate diversification into this sector as it would like to concentrate more on the Asian market (Apple Inc, 2011). As below-
The External Assessment
External audit
The external audit is also assessed by the external scopes and challenges (Sooper Tutorial, 2009). That are-
PEST analysis
PEST analysis is highly effective for analyzing the external environment where Apple’s iPhone is competing whether it is the domestic market or a foreign one. Thus, this analysis enables the firm to consider various aspects of macro-marketing variables within the contexts of political and legal, economic, socio-cultural and technological factors (Griffin, 2006). Such as

- Political factors: – Regarding political factors, Apple’s iPhone considers the stability of government in both national and international operations expanded in Europe and Asia. Additionally, trade and market policy, and trade agreements with the government are also significant.
- Economic factors: – Economic factors involve long and short-term economic trends not only in the USA but also in Japan, France, Scandinavia and West Germany, etc. Inflation and employment rate, GNP and GDP, and rate of exchange are also significant.
- Socio-cultural factors: – Socio-cultural factors are most influential for basically international operations regarding religion, language, demographic data and ethical involvement, etc.
- Technological factors: – Finally, technology is foremost for Apple’s i-Phone since it is running within a high growth of technological age. Quality, innovativeness, user friendliness are some essential featured of its technological environment (Freedman and Vohr, 1998).
Porter’s 5 forces model of competition
Threat for new entrants for mobile or smartphone devices is comparatively low for those companies which are already serving the electronics segment as Apple doing. Higher capital investment, R and D and product development costs are some specific reasons for such entry barriers.
Suppliers of this industry are powerful enough and can influence producers’ performance with a higher prices and inferior quality of raw materials.
On the other hand, the threat of substitute for Apple’s iPhone product is very high because many firms in the industry try to introduce new upgrade substitute products like Nokia introduced Nokia N97.
Buyers are also powerful since they want newer requirements and features to be installed on their mobile phones, laptops or PCs. Many firms are following disintermediation for diminishing the power of customers, like- Motorola and Dell. Various substitutes of cell phones are limited to landline and VOIP (Voice over Internet Protocol). PC market also has limited alternatives.
Finally, Apple’s iPhone has to compete with a number of strong rivals in PC segment, like- Dell, Microsoft, and Intel. The mobile phone segment involves Motorola, Nokia, and Samsung etc. (Freedman and Vohr, 1998).
BCG Matrix of Apple
Apple can categorize its iPhone segment by using the Boston- consulting group approach since BCG Matrix is a strategic portfolio planning, where the business units of production are classified into four different groups in accordance with market growth and related share (David, 2008). However, the following figure will demonstrate four specific groups as it is a useful tool to determine the business position in terms of the profitability of Apple.
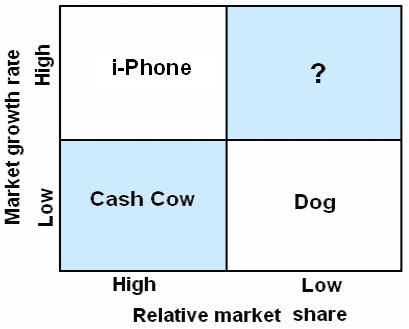
According to the situation of a Cash cow, the market growth of a Cash cow is small though the relative market share is high, therefore, it should require less investment than Dogs to sustain in a market where Apple’s position is not to match with the position of Cash Cow. On the other hand, Dog occupies the worst position because both its market share and growth rate are not satisfactory.
In contrast, the position of Question marks indicates high growth and low-shared firms; consequently, it necessitates abundant resources of cash to continue its operation and move alone to increase them.
The segment of Apple’s iPhone is the most significant part in this case, which is located in the upper part of the left-hand side of the diagram. This figure, it demonstrates that iPhone is now in the highest position in the matrix and it shows that iPhone occupies a larger market share with a better growth rate than all of its competitors in the global smartphone market. Therefore, it should necessitate low investment than others and, it can hold a perfect market share for a long time by implementing its strategic decisions.
External Factor Evaluation (EFE) matrix for i-phone
This matrix is used to accumulate competitive intelligence data from the external setting of the company. The same variables as mentioned in the external audit section are measured here (Sooper Tutorial, 2009), such as-
CPM
In the Competitive Profile Matrix, the company reflects on all of the internal as well as external factors to assess its success variables against the major competitors (Sooper Tutorial, 2008). As-
TOWS Matrix
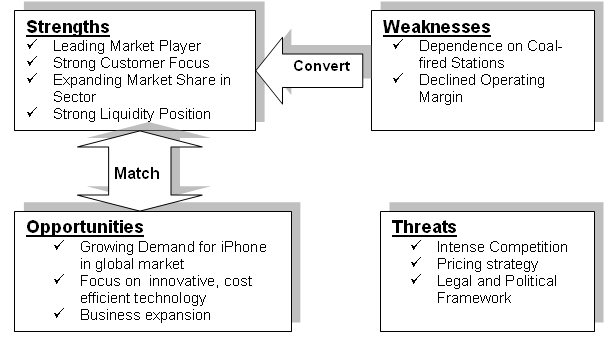
TOWS Matrix indicates the scope of the business to facilitate the external threats and opportunities comparing with internal weakness and strengths. As a market leader with brand value, and innovative technology, Apple enjoys its strength by modernization of services and capturing the US market the in Smartphone sector. Here, high prices, increased debt, expensive technology, low operating margin, and dependence on resellers stand as its weakness. However, the following figure explains mire elaborately
Figure 8: TOWS Strategic Framework for Apple Inc. Source: Self-generated from Weihrich (2010).
Select a Strategy
Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM)
This matrix is quite similar as the IFE matrix with some exceptions (Sooper Tutorial, 2009). Such as-
Here, Attractiveness Score: 1 = not acceptable;
Attractiveness Score 2 = possibly acceptable;
Attractiveness Score 3 = probably acceptable;
Attractiveness Score 4 = most acceptable;
According to the matrix, Apple has enough capability to expand its iPhone business in international market as well as it can continue its business in national market.
Strategic Implementation and Control
Apple should try to implement the suggested strategies as it has a strong financial base to adopt these strategies in the future operation of the products in the global market. However, this report has concentrated on the external opportunities and threats to find out its prospective sectors and related problems. Illegal production or production of similar products without patents, slow development of the retail sector, unsafe investment in the retail sector, and intense competition are the key problems of the company, it should require taking some initiatives. Apple should increase gradually the opening of retail stores to increase i-phone sales though increasing numbers retail stores is the subject of huge investment, but it must focus on its internal control system to avoid any uncertain situation in the case of marketing.
However, managers must arrange a quarterly meeting with retailers and periodically visit stores to assess performance and the gradual improvement, iPhone sales position, and current financial and marketing status of the stores. It has to identify the operational barriers and address any negative trends to bring future success; therefore, the top management, HR managers, and other regular staff will act as a team in order to control operation departments, manage selection departments, and arrange training programs. In addition, the management should review the strategies and market survey reports to widen the features of its iPhone products as competitors are always eager to launch innovative features in their Smartphone items. However, financial and non-financial benefits are two major benefits of this management while ethics should be incorporated from the mission to all sorts of the corporate culture. Finally, the marketer of this company should identify the uncertainty in terms of return on investment capital and survey the market frequently to collect feedback from the customers.
Reference List
Android Tapp. (2010) Total U.S. Market & Smartphone Market. Web.
Apple Inc. (2010). Annual report 2010 of Apple Inc: Form 10-K. Web.
Apple Inc. (2011). Apple Computer. Web.
Chen, H. et al. (2010). Marketing Analysis- Apple iPhone 3GS. Web.
David, F. (2008). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. (12th ed.). London: Prentice Hall.
Freedman & Vohr. (1998). Apple Computer Inc. Web.
Griffin, R. W. (2006). Management. (8th ed.). New York: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Johansson, J. K. (2008). Global Marketing. (4th ed.). New Delhi: Tata McGraw- Hill Publishing Company Limited.
Kotler, P. & Keller, K. L. (2006). Marketing management. (12th ed.). New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Sooper Tutorial. (2008). CPM-Competitive Profile Matrix. Web.
Sooper Tutorial. (2009). Apple External Factor Evaluation (EFE) Matrix. Web.
Weihrich, H. (2010). The TOWS Matrix — A Tool for Situational Analysis. Web.
WorldPress. (2011). Apple Computer. Web.
Footnotes
- Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States).
- Global System for Mobile.
